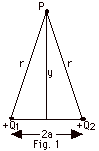
The homework is due on Wednesday, May 22nd.
You should Work on it individually.
For purposes of neatness and simplicity of grading, you should do the homework on an A-4 paper. However, use your exercise book as a scrapbook.
All answers should be written using a pen. Do not use a pencil. If you make an error, strike a line through it and correct it on the next line.
Determine the electric potential due to two point charges, Q1 and Q2, along a perpendicular bisector at point P of the line joining the charges. (b) What is the potential at P when r > > a?
Find (a) the electric potential at point P in Fig. 2 below. (b) Find the work done in bringing up a charge of +3 nC from infinity. (c) Repeat (a) and (b) for q2 = +1 nC.
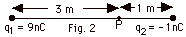
An alpha particle (charge +2e) approaches a gold nucleus (charge +79e) from a very great distance, starting with kinetic energy K. The alpha particle just touches the surface of the nucleus (the radius of the gold nucleus is 7.0 × 10 − 15 m) where its velocity is reversed. Find the initial kinetic energy of the alpha particle. A constant electric field E = 200 N/C exists between two parallel plates which are separated by 0.50 m.
How much work is done to carry a charge of 2μC from the negative plate to the positive plate without increasing its kinetic energy?
What is the potential energy difference between the plates?
What is the potential difference between the plates?
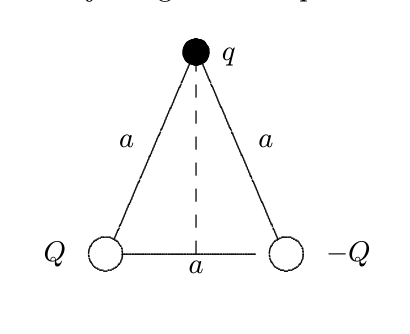
Two particle with charges Q and -Q are fixed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with sides of length a. What is the work required to move a particle with charge q from the other vertex to the center of the line joining the fixed particles?
In separate experiments, four different particles each start from far away with the same speed and impinge directly on a gold nucleus. The masses and charges of the particles are
particle 1: mass m0, charge q0
particle 2: mass 2m0, charge 2q0
particle 3: mass 2m0, charge q0/2
particle 4: mass m0/2, charge 2q0
Rank the particles according to the distance of closest approach to the gold nucleus, from smallest to largest. Explain why. Two conducting spheres, one having twice the diameter of the other, are separated by a large distance compared to their diameters. The smaller sphere (1) has charge q and the larger sphere (2) is uncharged. If the spheres are then connected by a long thin wire, what happens to the potential on each sphere?
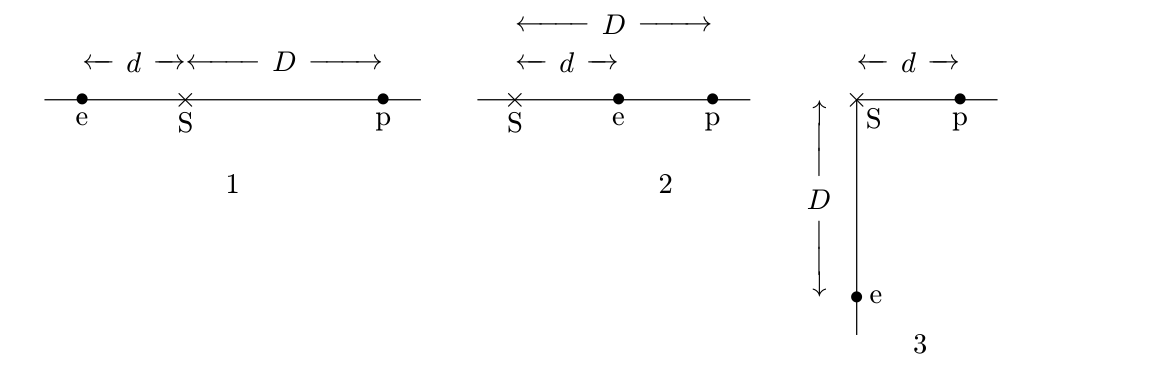
Three possible configurations for an electron e and a proton p are shown below. Take the zero of potential to be at infinity and rank the three configurations according to the potential at S, from most negative to most positive.
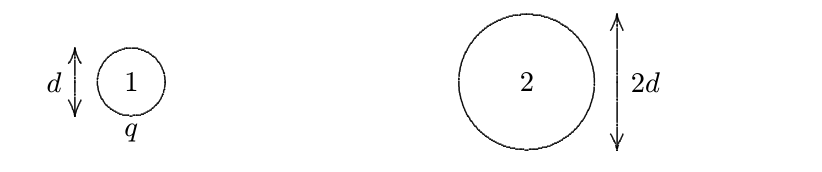
A 5-cm radius conducting sphere has a surface charge density of 4 × 102 C/m 2 on its surface. What is its electric potential, relative to the potential far away? An electric dipole is oriented parallel to a uniform electric field, as shown below.
It is rotated to one of the five orientations shown below. Rank the final orientations according to the change in the potential energy of the dipole-field system, most negative to most positive.
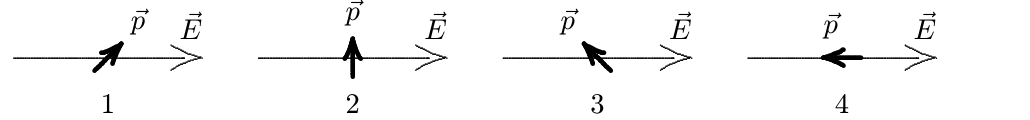
A point particle with charge Q is placed inside a cube but not at its center. Can the electric flux through any one side of the cube be computed using Gauss’s law? Draw a graph that represents the magnitude of the electric field as a function of the distance from the center of a solid charged conducting sphere of radius R?
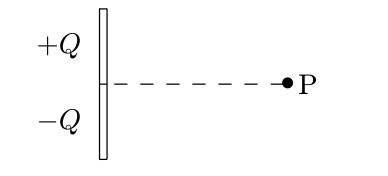
Positive charge + Q is uniformly distributed on the upper half a rod and negative charge − Q is uniformly distributed on the lower half. What is the direction of the electric field at point P, on the perpendicular bisector of the rod?
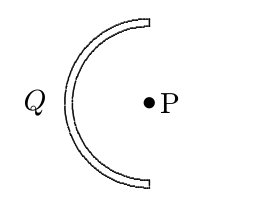
Positive charge Q is uniformly distributed on a semicircular rod. What is the direction of the electric field at point P, the center of the semicircle?
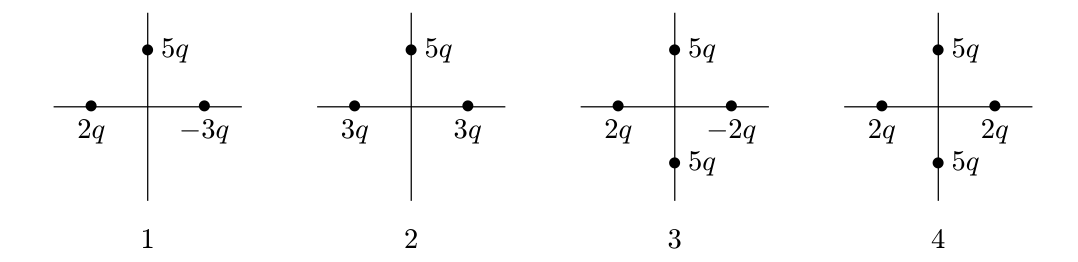
The diagrams below depict four different charge distributions. The charge particles are all the same distance from the origin. The magnetic electric field at the origin is the largest for which distribution? For which distributions is the electric field 0?
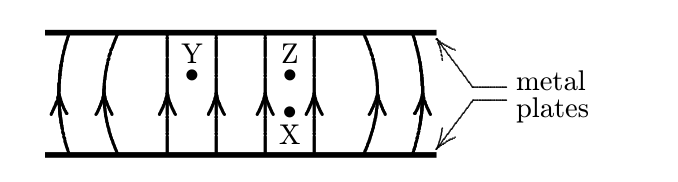
The diagram shows the electric field lines due to two charged parallel metal plates. What will happen if an electron is placed at X? What about a proton? Which plate is the positive plate?
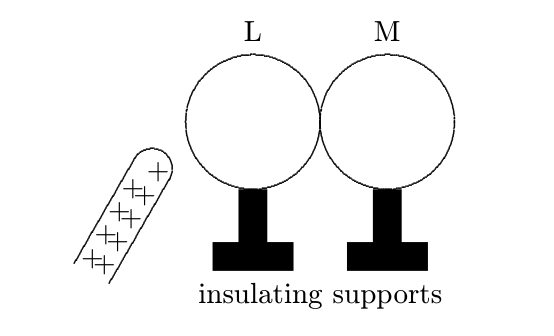
Two particles, X and Y, are 10 m apart. X has a charge of 2Q and Y has a charge of Q. What is the force exerted on Y by X? What are the units of k in $F=\dfrac{kQq}{r^2}$? Do a dimensional analysis for the units of k. Two uncharged metal spheres, L and M, are in contact. A negatively charged rod is brought close to L, but not touching it, as shown. The two spheres are slightly separated and the rod is then withdrawn. What is the final charge of the spheres?
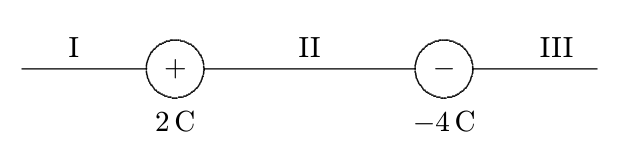
Two charged particles are arranged as shown. In which region could a third particle, with charge +1 C, be placed so that the net electrostatic force on it is zero?
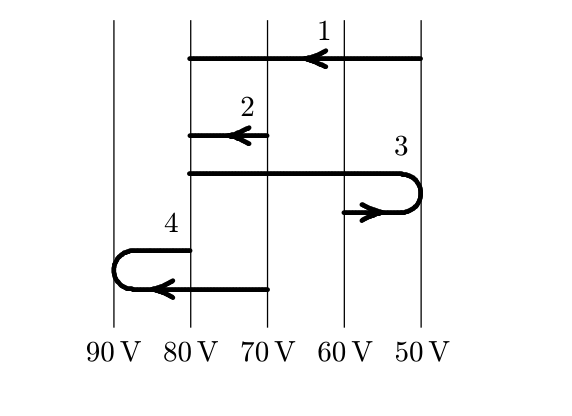
An electron goes from one equipotential surface to another along one of the four paths shown below. Rank the paths according to the work done by the electric field, from least to greatest.
The electric field in a region around the origin is given by E⃗ = M(xî + yĵ), where M is a constant. What are the equipotential surfaces in that region?